What is an FSSAI registration and license?
The FSSAI license is mandatory for food businesses in India, ensuring compliance with safety standards and regulatory requirements.
What is FSSAI License
FSSAI Registration: This is the basic level of registration applicable to small food businesses, including petty food manufacturers, storage units, transporters, retailers, marketers, and distributors. The turnover of these businesses should not exceed ₹12 lakhs per annum. The registration process involves filling out Form A and submitting the necessary documents to the local FSSAI office. Upon successful verification, a registration certificate is issued, which needs to be displayed prominently at the place of business.

Food Business Operators (FBOs) Who Require FSSAI Registration
- Petty retailers and retail shops such as a retail shop, snacks shop, confectionery or bakery, etc.
- Temporary stalls or fixed stall or food premise involved in the preparation, distribution, storage and sale of food products such as Gol Gappa stall, chat stall, fruits/vegetable vendors, tea stall, snacks stall, bread pakoda stall, samosa stall, chinese food stall, South Indian food stall, sweet stall, juice shops, etc.
- Hawkers who sell packaged or freshly prepared food by travelling (usually on foot or movable carts) from one location to another.
- Dairy units including milk chilling units, petty milkman and milk vendors.
- Vegetable oil processing units.
- Slaughtering houses such as meat shops, mutton shops, chicken shops, lamb meat, etc.
- Meat processing and fish processing units.
- All food manufacturing or processing units that include repacking of food.
- Proprietary food and Novel food.
- Cold/refrigerated storage facility.
- Transporter of food products having a number of specialised vehicles like insulated refrigerated van/wagon, milk tankers, food wagons, food trucks, etc.
- Wholesaler, supplier, distributor and marketer of food products.
- Hotels, restaurants and bars.
- Canteens and cafeteria including mid-day meal canteens.
- Food vending agencies and caterer.
- Dhaba, PG providing food, Banquet halls with food catering arrangements, home based canteens and food stalls in fairs or religious institutions.
- Importers and exporters of food items including food ingredients.
- E-commerce food suppliers including cloud kitchens.
- The type of FSSAI license/registration required by each of the kinds of the above-mentioned businesses depends on their eligibility criteria. The eligibility criteria for each kind of business and type of license/registration is provided on the FSSAI
Types of FSSAI Registration
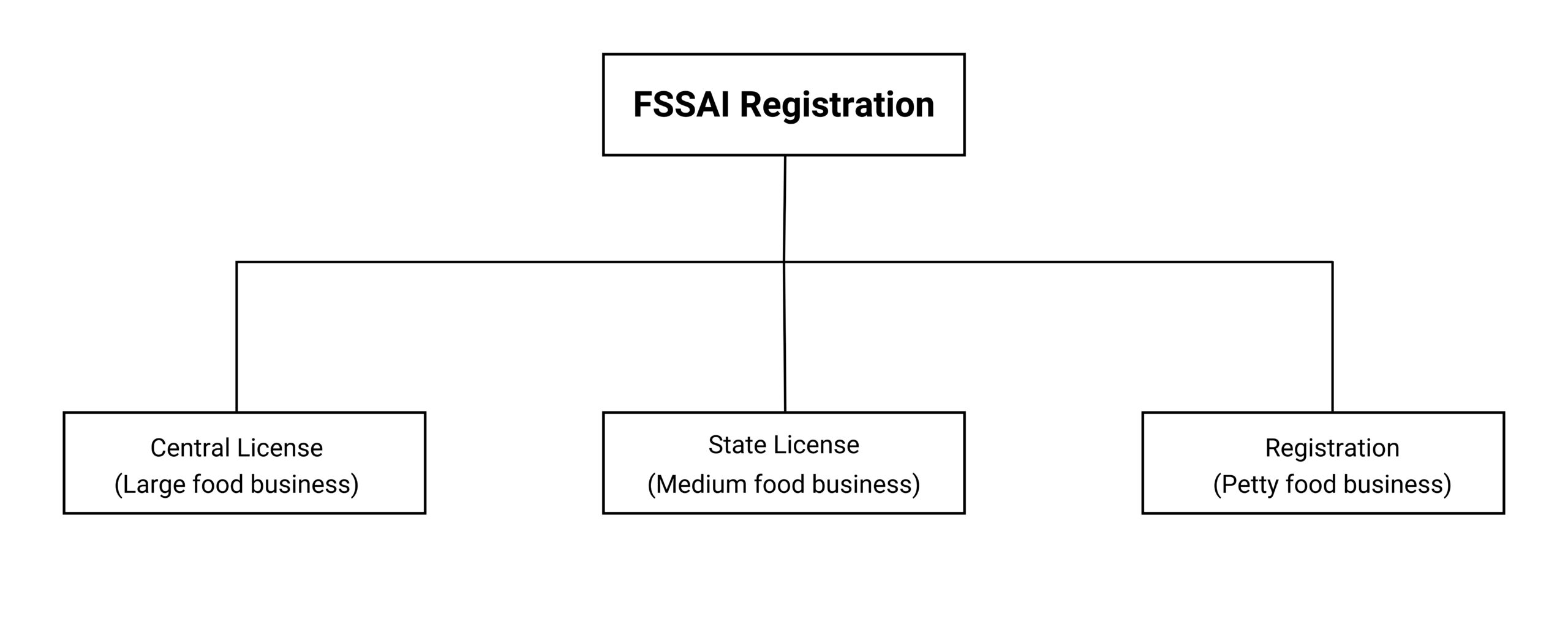
- FSSAI Basic Registration – FBOs having a turnover of less than Rs.12 lakh p.a must obtain FSSAI basic registration. The FSSAI registration form that the applicant has to fill to obtain FSSAI basic registration is Form A.
- FSSAI State License – FBOs having a turnover of more than Rs.12 lakh p.a and less than Rs.20 crore p.a must obtain the FSSAI state license. The FSSAI registration form that the applicant has to fill to obtain an FSSAI state license is Form B.
- FSSAI Central License – FBOs having a turnover of more than Rs.20 crore p.a must obtain the FSSAI central license. The FSSAI registration form that the applicant has to fill to obtain FSSAI central license is Form B.
Benefits FSSAI Registration
Legal Compliance:
Ensures compliance with food safety laws and regulations, avoiding legal penalties and business disruptions.
Consumer Trust:
Enhances consumer confidence by demonstrating adherence to quality and safety standards, potentially increasing sales.
Business Expansion:
Facilitates access to wider markets, including retail chains and export opportunities, due to recognized standards.
Product Quality Assurance:
Promotes better quality control and hygiene practices, safeguarding against foodborne illnesses and ensuring customer satisfaction.
Procedure for Obtaining FSSAI Registration Online
FSSAI Registration Eligibility
FSSAI Registration is a basic license and it is required for all the FBOs involved in the small-scale food business. This category covers the following businesses:
- Any FBO with an annual turnover of not more than Rs. 12 lakh.
- Petty retailer dealing in food products.
- Any person who manufactures or sells any food article by himself.
- Food sale is done by the temporary stall holder.
- Any individual who distributes food in any religious or social gathering except a caterer.
- Small-scale or cottage industries dealing in the food business.
- Small businesses having the following food capacity limits:
FSSAI License Cost
The applicant/FBO needs to pay the fees while submitting the FSSAI registration form. The FSSAI registration fee for different types of registration are as follows:
- FSSAI Basic Registration – Fee of Rs.100
- FSSAI State License – Fee between Rs.2,000 to Rs.5,000 (Depends on the type of business carried out)
- FSSAI Central License – Fee of Rs.7,500
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Any registered or licensed person under the FSSAI has to adhere to the rules and regulation under the FSS Act, 2006. Food safety officer generally conducts the inspection of the food business operator’s facility and identifies the level of compliance with the regulation using a checklist. Based on the compliance level, the food safety officer marks it as:
- Compliance (C)
- Non-compliance (NC)
- Partial compliance (PC)
- Not applicable/Not observed (NA)
Based on the above, the food safety officer might issue an improvement notice where ever required per Section 32 of the FSS Act, 2006. If the business operator fails to comply with the improvement notice, the officer after giving the licensee an opportunity to show cause may cancel his license. Any food business operator aggrieved by an improvement notice can appeal to the State Commissioner of Food Safety. The decision thereon can be challenged through appealing to the Food Safety Appellate Tribunal/High Court.
Penalty for Non- Compliance
Listed is the penalty for various type of non-compliance:
Sl.No | Particulars | Fine |
1 | Food quality not in compliance with ac | 2 Lakh Petty manufacturer – 25,000/- |
2 | Sub-standard food | 5 Lakh |
3 | Misbranded Food | 3 Lakh |
4 | Misleading advertisement or false description | 10 Lakh |
5 | Extraneous matter in food | 1 Lakh |
6 | Failure to comply with Food safety officer direction | 2 Lakh |
7 | Unhygienic processing or manufacture | 1 Lakh |
Frequently Asked Questions
FSSAI Stands for “Food Safety and Standard Authority of India. FSSAI is an Independent organization under the Ministry of Health. FSSAI Registration is mandatory for every individuals or entity that is eligible for an FSSAI food safety Registration or License.
Maintaining the food quality levels in order to ensure safety and providing satisfaction to every consumer is the aim of every Food Business Operator. Food safety and standards authority of India (FSSAI Registration) plays an important role in formulating the controlling procedures.
There are 4 steps including fssai license registration procedure that are following:-
- Selection of Kind of Business
- Selection of Food Category
- Selection of Type of License
- Documentation
- Issue of Certificate
Common Documents Required for Obtaining FSSAI Registration
- FSSAI declaration
- Photo Identity of FBO
- Proof of possession of premises (eg. Rental Agreement)
- Partnership Deed / Certificate of Incorporation / Articles of Association etc.
- List of food products to be dealt with.
- Food safety management system plan
- Basic registration: It Includes Business Having Turnover up to 12 Lakh in a Year
- State license: Business having turnover between 12 lakh to 20 cr in a year comes under state license
- Central license: Business having turnover above 20 cr comes under central license, any business doing export and import also come under central license
FSSAI has extended its scope to include the applications of e-commerce food services. This category includes delivery services such as Uber Eats, Swiggy and Zomato and online grocery stores such as amazon, Big Basket, etc. Of late, the food e-commerce sector has grown tremendously. As these platforms operate widely, it is important for these services to ensure compliance with FSSAI.
- Cleaning :- Working area and equipment/ utensils should be cleaned appropriately.
- Water Supply :- There should be an adequate supply of potable water. The water should be examined chemically and bacteriologically by a NABL accredited laboratory. Ice and steam wherever in use should be made from the same portable water.
- Raw Materials :- Certain FSSAI guidelines should be followed in the handling and preparation of raw materials
- Raw meat and processed meat should be kept separate from other food items.
- The used surface should be adequately cleaned with anti- bacterial agents.
